Chagas Disease Heart Failure
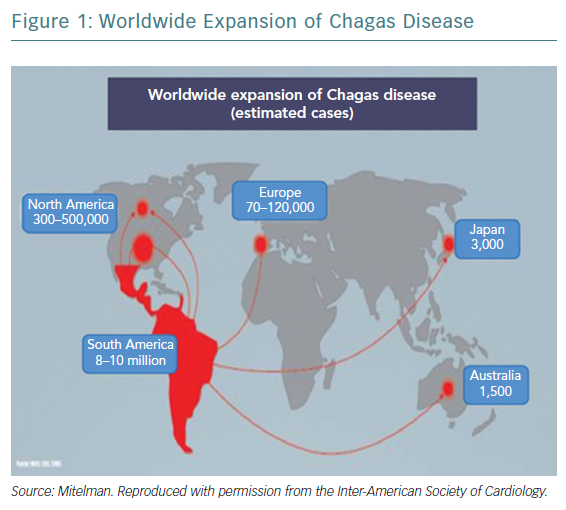
Chagas disease heart failure. Chagas disease originally a South American endemic health problem is expanding worldwide because of people migration. Cardiac involvement which typically appear. Chagas heart disease is multifactorial and can include dilated cardiomyopathy thromboembolic phenomena and arrhythmias that may lead to sudden death.
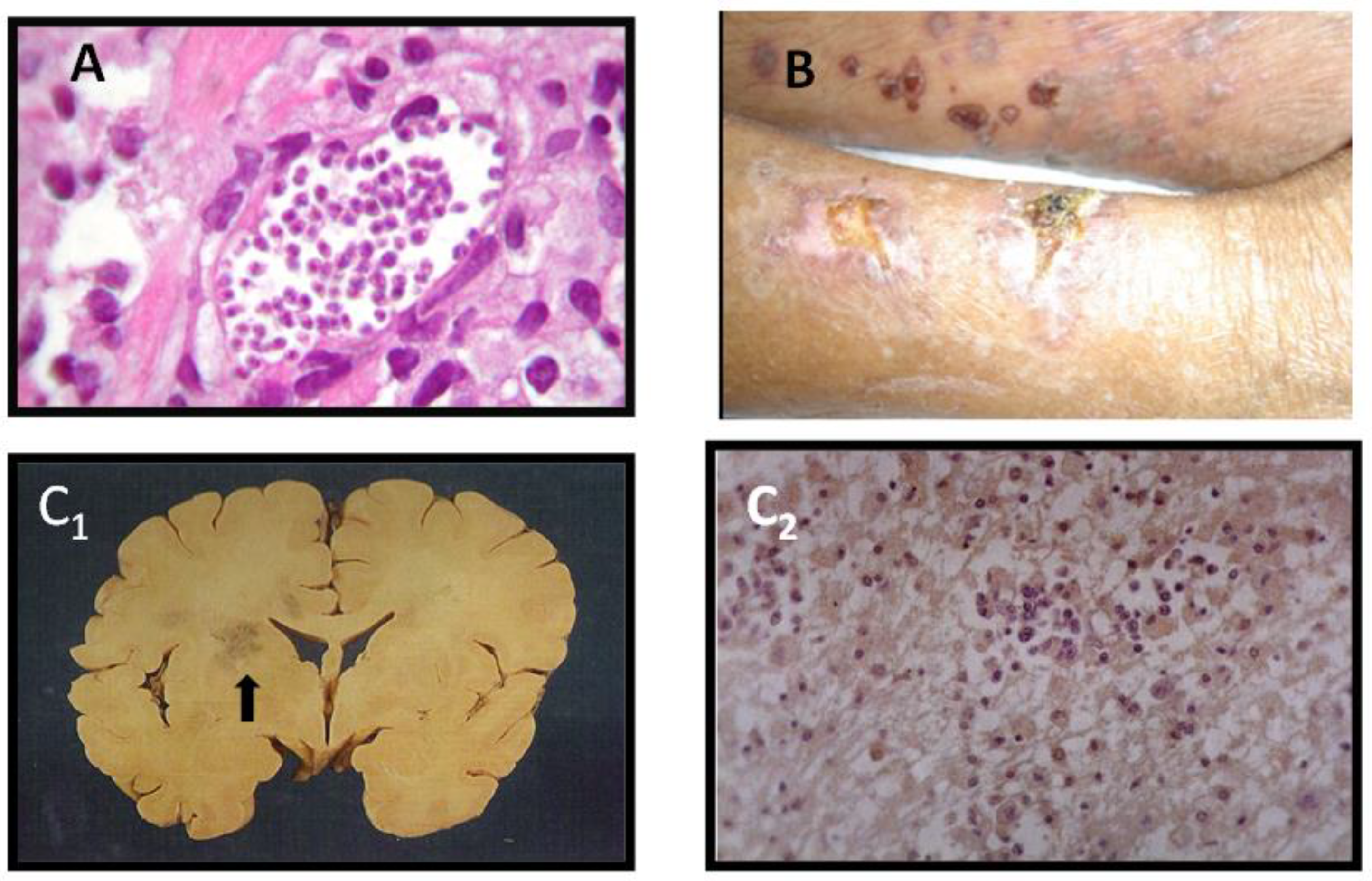
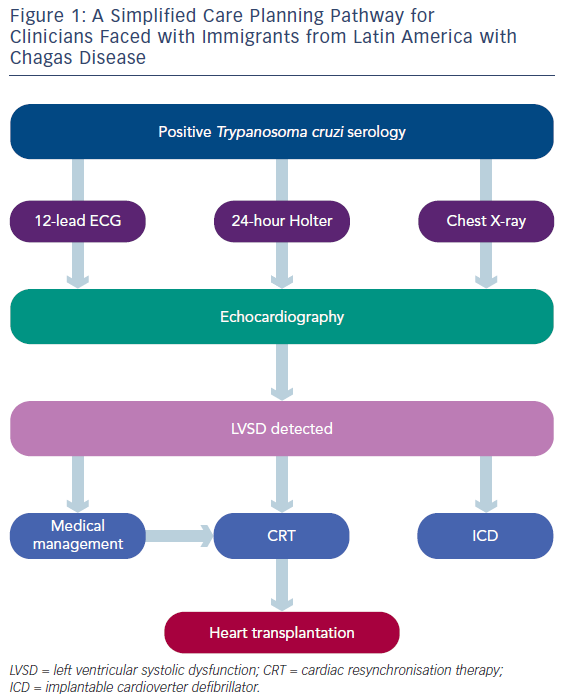
Chagas disease is caused by a protozoan parasite Trypanosoma cruzi that is transmitted to humans through the feces of infected bloodsucking insects in endemic areas of Latin America or occasionally by nonvectorial mechanisms such as blood transfusion. Pathogenic pathways are mainly related to inmunoinflamatory reactions in the myocardium and less frequently. Value of echocardiography for diagnosis and prognosis of chronic Chagas disease cardiomyopathy without heart failure Echocardiography was useful both to characterise and to determine the prognosis of patients with chronic Chagas disease without heart failure.
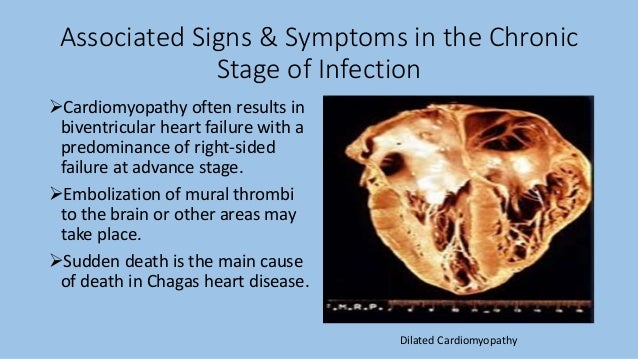
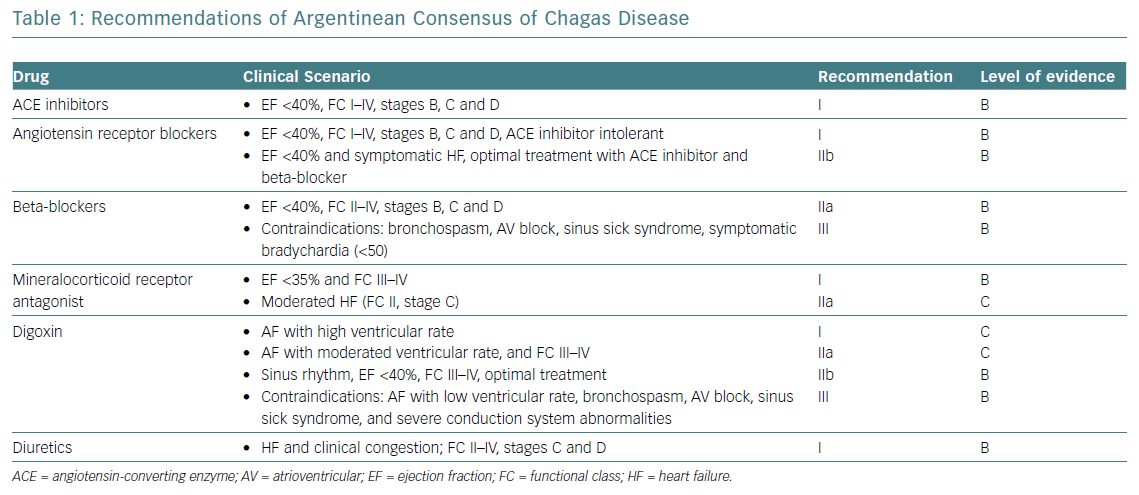
Early diagnosis and treatment are important to improve survival rates and quality of life. Chagas cardiomyopathy represents the most frequent and serious complication of chronic Chagas disease affecting about 20-30 of patients potentially leading to heart failure arrhythmias thromboembolism stroke and sudden death. In general the heart failure manifests itself between thirty and forty years of age.
Chagas heart disease a form of a dilated cardiomyopathy caused by Trypanosoma cruzi is a major cause of cardiovascular related death in endemic areas. Chagas disease resulting from the protozoan Trypanosoma cruzi is an important cause of heart failure stroke arrhythmia and sudden death. Pathogenic pathways are mainly related to inmunoinflamatory reactions in the myocardium and less frequently.
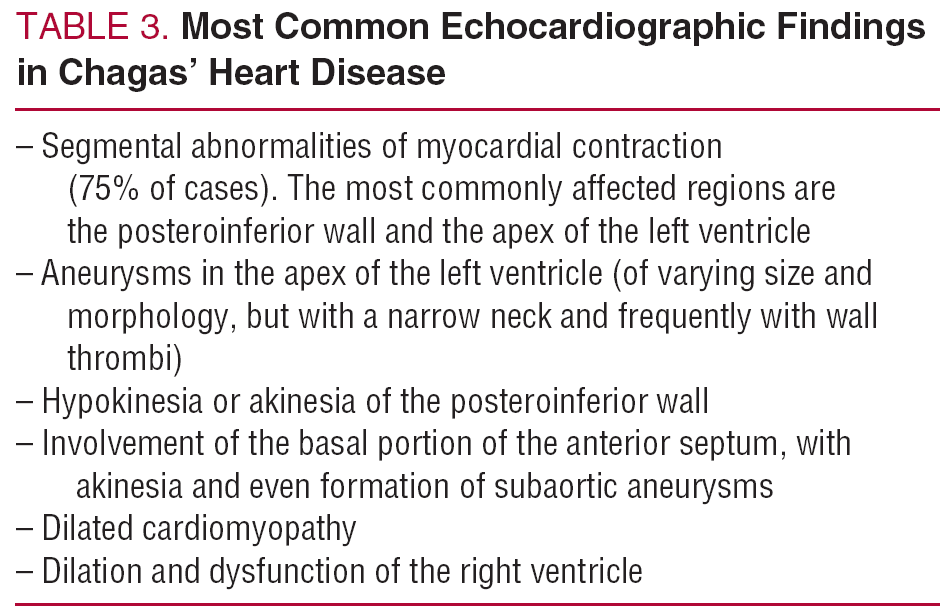
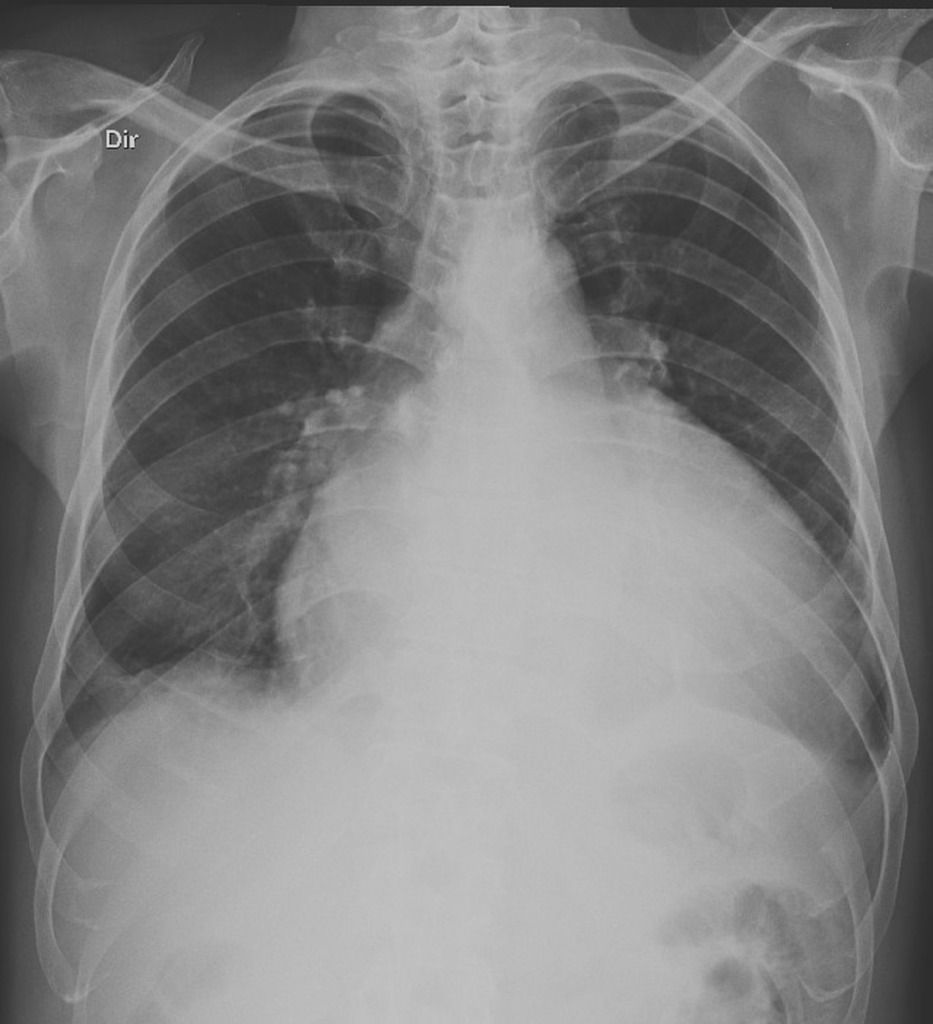
Although Chagas disease occurs significantly less often in Switzerland physicians should be aware of the disease especially in times of increased migration and mobility. Chagas disease has characteristics of an endemic disease and is an important cause of dilated heart disease and heart failure HF in regions of low socioeconomic level leading to high mortality and morbidity rates. Intraventricular conduction system abnormalities ventricular arrhythmia sinus node dysfunction left ventricular segmental lesions and enlargement.
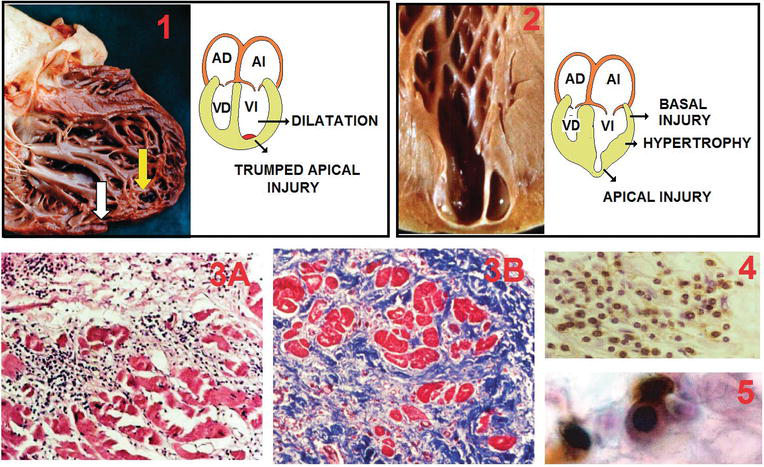
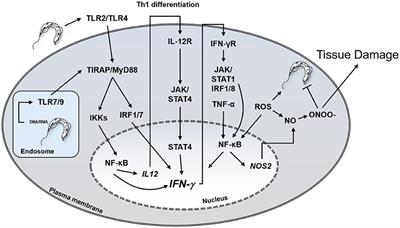
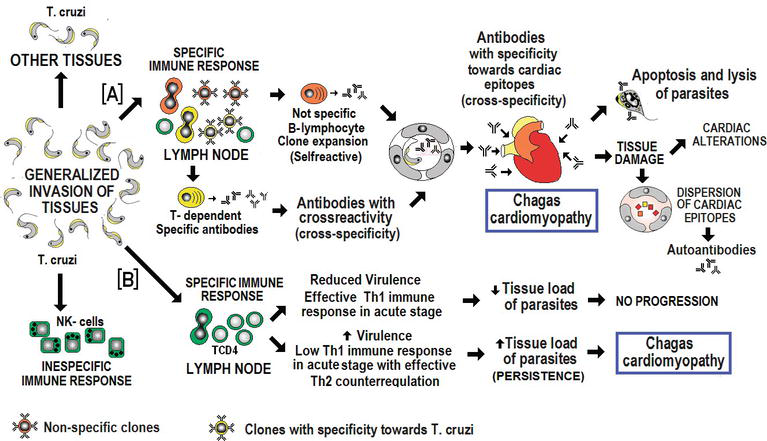
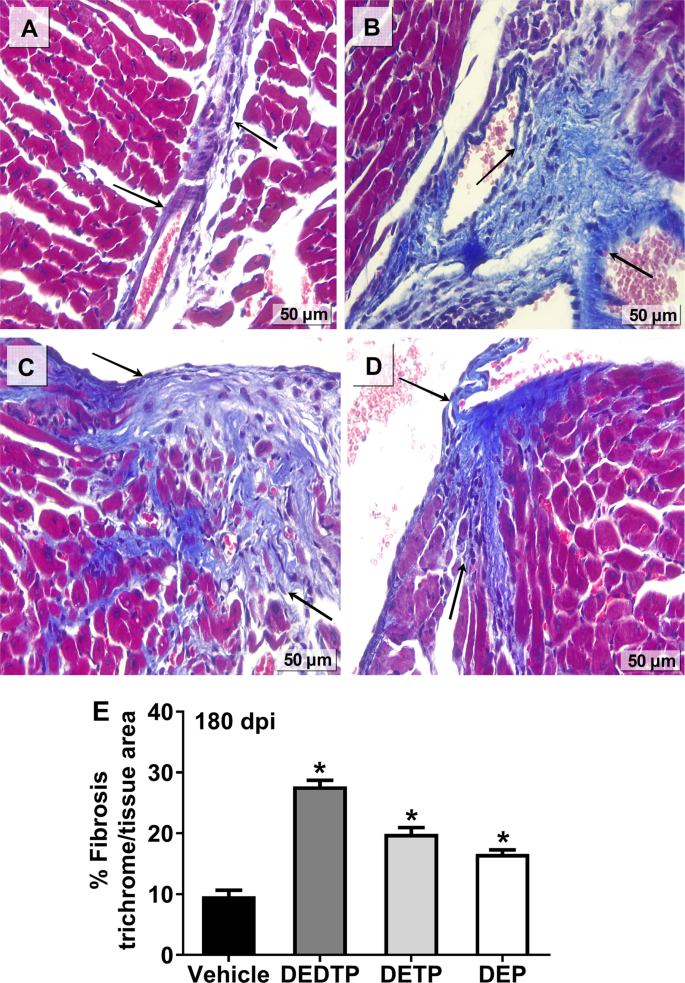
Traditionally regarded as a tropical diseas. The anatomic background of chronic Chagas disease is a progressive fibrotic and diffuse chronic myocarditis that slowly destroys the myocardial fibers leading to heart failure. According to this hypothesis megaesophagus megacolon and cardiac dilation in Chagas disease are consequences of the denervation of the parasympathetic autonomous system whereas the myocardial inflammation should not be considered as an important element for cardiac failure.
Its main impact is on the cardiovascular system producing myocardial damage that frequently results in heart failure. Chagas heart disease is a form of dilated cardiomyopathy that often produces heart failure and people with this disease ought to receive all the standard treatments for dilated cardiomyopathy.
Chagas disease originally a South American endemic health problem is expanding worldwide because of people migration.
Its main impact is on the cardiovascular system producing myocardial damage that frequently results in heart failure. Intraventricular conduction system abnormalities ventricular arrhythmia sinus node dysfunction left ventricular segmental lesions and enlargement. Chagas heart disease a form of a dilated cardiomyopathy caused by Trypanosoma cruzi is a major cause of cardiovascular related death in endemic areas. In general the heart failure manifests itself between thirty and forty years of age. Chagas disease resulting from the protozoan Trypanosoma cruzi is an important cause of heart failure stroke arrhythmia and sudden death. Chagas disease has characteristics of an endemic disease and is an important cause of dilated heart disease and heart failure HF in regions of low socioeconomic level leading to high mortality and morbidity rates. Chagas heart disease CHD is also the most common cause of cardiomyopathy in Latin America and in endemic areas it is the leading cause of cardiovascular death among patients aged 30-50 years Rassi Jr. Although Chagas disease occurs significantly less often in Switzerland physicians should be aware of the disease especially in times of increased migration and mobility. Chagas disease originally a South American endemic health problem is expanding worldwide because of people migration.
The anatomic background of chronic Chagas disease is a progressive fibrotic and diffuse chronic myocarditis that slowly destroys the myocardial fibers leading to heart failure. Chagas disease originally a South American endemic health problem is expanding worldwide because of people migration. The anatomic background of chronic Chagas disease is a progressive fibrotic and diffuse chronic myocarditis that slowly destroys the myocardial fibers leading to heart failure. Its main impact is on the cardiovascular system producing myocardial damage that frequently results in heart failure. Although Chagas disease occurs significantly less often in Switzerland physicians should be aware of the disease especially in times of increased migration and mobility. The clinical presentation of the disease is highly variable from general symptoms to severe cardiac involvement that can culminate in heart failure. According to this hypothesis megaesophagus megacolon and cardiac dilation in Chagas disease are consequences of the denervation of the parasympathetic autonomous system whereas the myocardial inflammation should not be considered as an important element for cardiac failure.













/chagasdisease-symptoms-5ada07b2a474be00360a271b-1ae2a314d0de4347a9becd72384cf392.png)





















Post a Comment for "Chagas Disease Heart Failure"